The explosive growth of advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs), particularly cellular therapeutics, has driven steady investment in facilities capable of manufacturing these therapeutics at scale . Meanwhile, the industry is collectively moving to adapt to European Union Annex 1 standards, which places a more stringent emphasis on contamination control.

Downloads
Repurposing a US Cell Therapy Facility for Flexibility and EU Compliance
Cover: The explosive growth of advanced therapy medicinal products (ATMPs), particularly cellular therapeutics, has driven steady investment in facilities capable of manufacturing these therapeutics at scale. Meanwhile, the industry is collectively moving to adapt to European Union Annex 1 standards, which places a more stringent emphasis on contamination control.
Pharma Facilities, Composable Tools, and Validation 4.0
Feature: The pharmaceutical industry stands at the precipice of a revolution as emerging digital technologies provide new opportunities to boost productivity through continuous process improvements. The Pharma 4.0™ framework, an adaptation of the broader Industry 4.0 movement, aims to transform how drugs are produced and delivered.
Gene Editing and Facility Retrofits for Crispr and Beyond
Feature: With the approval of the first gene edited therapeutic in 2023, production of gene edited therapies is accelerating, introducing tough decisions for manufacturing development. Gene editing therapy production is complex, o en involving multimodality manufacturing operations in one facility to produce a single therapeutic. This article considers whether retrofitting an aging monoclonal antibody (mAb) facility for the manufacture of a gene editing therapy could be a solution.
Acceptable Discoloration Levels on Pharmaceutical Weld Beads
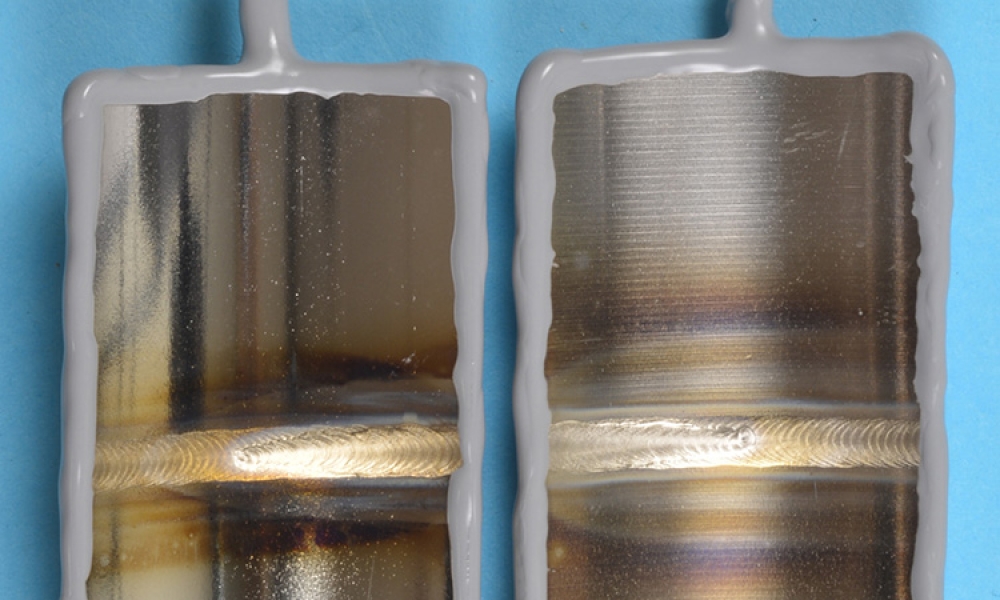
Technical: Welds used in biopharmaceutical manufacturing must meet critical criteria to maintain a defined level of purity and bioburden control. One highly debated area of concern is the level of discoloration allowable on the product contact surfaces in the welded condition and secondary finishing methods. This article addresses the studies commissioned by the American Society for Mechanical Engineers (ASME) to determine the allowed discoloration in the heat affected zone (HAZ) and weld bead.
Artificial Intelligence Governance in GxP Environments
Technical: companies, providing support from drug discovery through manufacturing. The nature of AI and concerns of bias, privacy, transparency, and security in a regulated industry necessitate a governance framework to ensure concerns are controlled using “guardrails.” These guardrails ensure the quality, privacy, and security of data used in AI applications. This article provides a recommended approach to implementing guardrails through several policies and procedures and discusses AI governance, which defines data ownership, consent, and access policies and procedures.
In This Issue
As we get into the peak of the summer months and everyone is preparing for a well-deserved vacation, ISPE is in full swing. We just had a great Biotechnology Conference in Boston. Attendees heard about topics ranging from the use of digitization and artificial intelligence in manufacturing to quality systems maturity and the quality culture required to manufacture safe and efficacious...
The 2024 ISPE Annual Meeting & Expo will be held 13–16 October in Orlando, Florida, and virtually. David Churchward is the conference’s Executive Chair. He offers advice and shares what attendees can expect at the upcoming conference.
Every year we celebrate the achievements of state-of-the-art pharmaceutical facility projects through the Facility of the Year Awards (FOYA). The buildings are beautiful, energy efficient, and sustainable; the...
In each issue of Pharmaceutical Engineering®, we introduce a member of the ISPE staff who provides ISPE members with key information and services. Meet Matt Lehmann, Custom Training Manager, Professional Development.
This year, the ISPE Foundation made great strides in its mission of fueling global health equity by fostering access to knowledge and nurturing diverse talent.
In 2019, ISPE released the Second Edition of the ISPE Baseline® Guide Vol 5: Commissioning and Qualification. This guide mirrors the industry’s evolution toward harmonizing with latest...
The new ISPE Good Practice Guide: Unique Identification of Glass Primary Containers in Pharmaceutical Fill and Finish Operations involved a cross-functional team of industry experts and professionals from parenteral/injectable medicine manufacturing. The team included industry competitors who worked together to establish a common approach. They provided a balanced, industrywide perspective on...
In April 2024, ISPE published the ISPE Guide: 503A Compounding - Regulatory Basis and Industry Good Practices for Pharmacies, adding to the growing body of knowledge ISPE is producing for the pharmaceutical compounding industry. Written by industry experts and reviewed by practitioners in the area, the guide provides an overview of relevant US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations and...
Rod Freeman started his career in the pharma-ceutical industry as an analytical chemist.
Growing up on a farm, Allen Koester thought he would design farm equipment after earning his degree in mechanical engineering.
Long gone are the days of early morning Women in Pharma breakfast meetings at ISPE international conferences—well, sort of. The long-awaited 2024 ISPE Annual Meeting & Expo is on the horizon and it’s time...
Artificial intelligence (AI) is used by pharmaceutical and biotech companies, providing support from drug discovery through manufacturing. The nature of AI and concerns of bias, privacy, transparency, and security in a regulated industry necessitate a governance framework to ensure concerns are controlled using “guardrails.” These guardrails ensure the quality, privacy, and security of data...
Welds used in biopharmaceutical manufacturing must meet critical criteria to maintain a defined level of purity and bioburden control. One highly debated area of concern is the level of discoloration allowable on the product contact surfaces in the welded condition and secondary finishing methods. This article addresses the studies commissioned by the American Society for Mechanical Engineers...
The expectations for room differential pressures to maintain air quality in pharmaceutical facility design are consistent and well defined from a regulatory perspective. However, there is no common approach to the design, monitoring, or alarming of area differential pressures. This article explores differential pressure concerns in aseptic manufacturing, or cleanroom classes B, C, and D.
On 25 August 2023, the long-awaited revision to Annex 1 became effective, introducing significant regulatory changes, including the requirement of a documented contamination control strategy (CCS). During a workshop at the 2023 ISPE Annual Meeting & Expo, 11 teams of attendees were presented with a risk-based methodology to develop and evaluate CCS elements focused on extrinsic...
Implementing advanced automation technologies is a strategic move that can amplify the positive outcomes of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives. By leveraging ESG initiatives, pharmaceutical companies can enhance their competitive edge and contribute positively to global sustainability efforts.
With the approval of the first gene edited therapeutic in 2023, production of gene edited therapies is accelerating, introducing tough decisions for manufacturing development. Gene editing therapy production is complex, often involving multi-modality manufacturing operations in one facility to produce a single therapeutic. This article considers whether retrofitting an aging monoclonal...
The pharmaceutical industry stands at the precipice of a revolution as emerging digital technologies provide new opportunities to boost productivity through continuous process improvements. The Pharma 4.0™ framework, an adaptation of the broader Industry 4.0 movement, aims to transform how drugs are produced and delivered.
Each year, ISPE recognizes innovation in pharmaceutical facilities with the Facility of the Year Awards (FOYA). The 2024 FOYA submission finalists were announced at the 2024 ISPE Aseptic Conference in Vienna, Austria. Finalists for the 2024 awards highlight the continued progress and innovation at play in pharmaceutical manufacturing worldwide and across modalities. From projects tailored to...
The ISPE International Company of the Year award recognizes outstanding leadership and support provided by a company, as reflected by significant active participation in the Society’s committees, Communities of Practice (CoPs), programs, and activities, as well as its support of employee participation in ISPE. The winner for 2023, Roche, was announced at the 2023 ISPE Annual Meeting & Expo...